Using the patented solid state Chromatrap® spin column technology, we offer a detailed genome-wide comparison of native and crosslinked chromatin immunoprecipitation, followed by next generation sequencing (ChIP-seq).
Background
This application note provides a comparison of the enrichment of the histone modification H3K4me3 from chromatin derived through the two different methods of extraction–native and cross link - across the genome. H3K4me3 was chosen for this study to highlight the efficiency and sensitivity of the Chromatrap® spin column technology for both methods of ChIP-seq. The histone mark is associated with ‘open’ transcription start sites and gene activation, and makes for an abundant epigenomic target as it is present in euchromatin throughout the genome.
Method
Chromatin preparation
Chromatin for N-ChIP and X-ChIP was prepared from the human endometrial epithelial cancer cell line Hec50, as per the Chromatrap® protocols.
For N-ChIP cells were lysed in Hypotonic Buffer, before the separated nuclei were subjected to micrococcal nuclease digestion. Following that the samples were dialysed to eradicate impurities and then processed for ChIP.
For X-ChIP samples were fixed in 1% formaldehyde before being re-suspended and lysed in Hypotonic Buffer.
The cells were spun down, supernatant discarded and the released nuclei were collected by centrifugation, lysed and the chromatin sheared to obtain 100 – 500 bp length fragments.
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation
For immunoprecipitation, slurries were prepared at a 5:2 chromatin: antibody ratio and incubated at 4°C for 1hr before immunoprecipitation with the Chromatrap® spin columns. Parallel to that inputs containing 5 µg chromatin were prepared for downstream analysis and not subject to ChIP enrichment. Following ChIP the X-ChIP samples were reverse cross-linked (2hrs) and subjected to proteinase K digestion, while the N-ChIP samples were immediately subjected to proteinase K digestion.
Prior to library preparation all of the samples were purified using Chromatrap® DNA purification columns.
Library preparation
Chromatrap® NEBNext® Ultra™ (NEB) library preparation kit and KAPA Biosystems (Roche) quantification kit for next generation sequencing (NGS) were used to prepare and quantify the libraries. To confirm sample size distributions were between 200-300 bp, samples were processed on an Agilent Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies).
Chromatrap® ChIP-seq analysis
Using the Illumina® MiSeq paired end high throughput sequencing was performed, and the quality of the data produced was analysed by FASTQC. ENCODE UCSC genome browser database and Bowtie2 were then utilised for sequence mapping and alignment of the human reference genome (hg19). The peak enrichment data were then run through the Chromatrap® ChIP-seq data analysis software, with input for both N and X-linked chromatin samples used as background/baseline. To visualise the H3K4me3 enrichment peaks for both the N-ChIP and X-ChIP samples, integrative genomics viewer online software was employed.
Results
High quality sequence scores were obtained from both N and X-linked ChIP, with Q scores greater than 30 and duplication rates below 5% across all samples. The Chromatrap® ChIP-seq Data Analysis software was used to analyse peak enrichment for Native and X-linked sequenced samples.
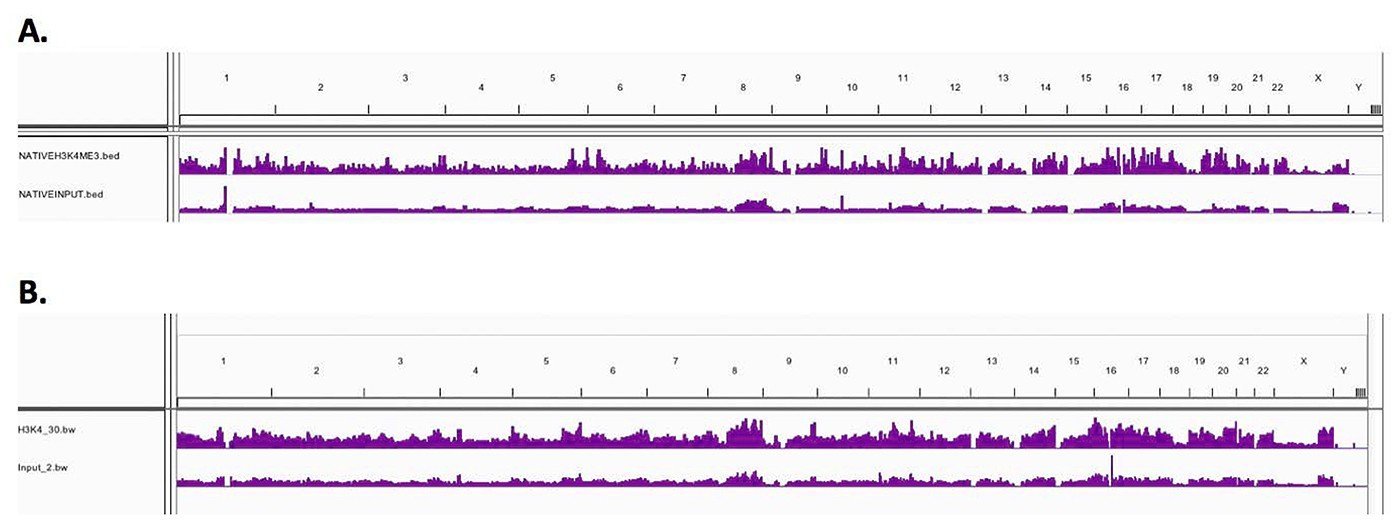
Low resolution genome wide IGV visualised peak enrichment showed comparable H3K4me3 peaks for both Native and X-linked chromatin samples, demonstrating that Chromatrap® immunoprecipitation is comparable and reproducible between N-ChIP and X-ChIP-seq on a genome wide scale, as illustrated by the peak maps below – (A) N-ChIP and (B) X-ChIP. Further validation of the homology between N-ChIP and X-ChIP-seq is observed when analysing specific gene loci.
Conclusion
Demonstrating strong and comparable enrichment of H3K4me3 from both Native and Cross-linked chromatin, we have highlighted that both Native and Cross-linked chromatin preparation methods are compatible with Chromatrap® extraction and capture technology. The wide range of ChIP assays available from Chromatrap® provides users with abundant flexibility and choice for different methods of chromatin preparation and enrichment for downstream next generation sequencing.
Ensure the highest quality ChIP assay for your research by equipping yourself with one of our revolutionary Chromatrap ChIP-seq kits - order today or get in touch with our team if you have any questions.

